1. Rated capacitance:
The capacitance value for which the capacitor has been
designed and which is usually indicated upon it.
2. Category temperature range:
The range of ambient temperatures for which the capacitor has been designed to operate continuously; This is defined by the temperature limits of the appropriate category.
3. Upper category temperature:
The maximum ambient temperature for which a capacitor has been designed to operate continuously.
4. Lower category temperature:
The minimum ambient temperature for which a capacitor has been designed to operate continuously.
5. Rated temperature:
The maximum ambient temperature at which rated voltage may be continuously applied.
6. Rated voltage:
The maximum direct voltage or the maximum RMS alternating voltage or peak value of pulse voltage which may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature between the lower category temperature and the rated temperature.
7. Category voltage:
The maximum voltage which may be applied continuously to a capacitor at its upper category temperature.
8. Temperature derating voltage:
For any temperature between the rated temperature and the upper category temperature, the temperature derating voltage is the maximum voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor.
9. Insulation resistance(IR) / Time constant (t) Insulation resistance (IR) / Time constant (t):
The insulation resistance is the ratio between an applied DC voltage and the resulting leakage current after a minute of charge. It is expressed in MΩ. The time constant is expressed in seconds with the following
formula:
t (s)=lR (MΩ)×CR (μF).
10. Pulse rise time (dv/dt):
The pulse rise time defines the capability of a capacitor to withstand high current peaks due to fast voltage changes. The peak current is defined by the following formula:
lp(A)=C(uF) × dv/dt ( V/μs)
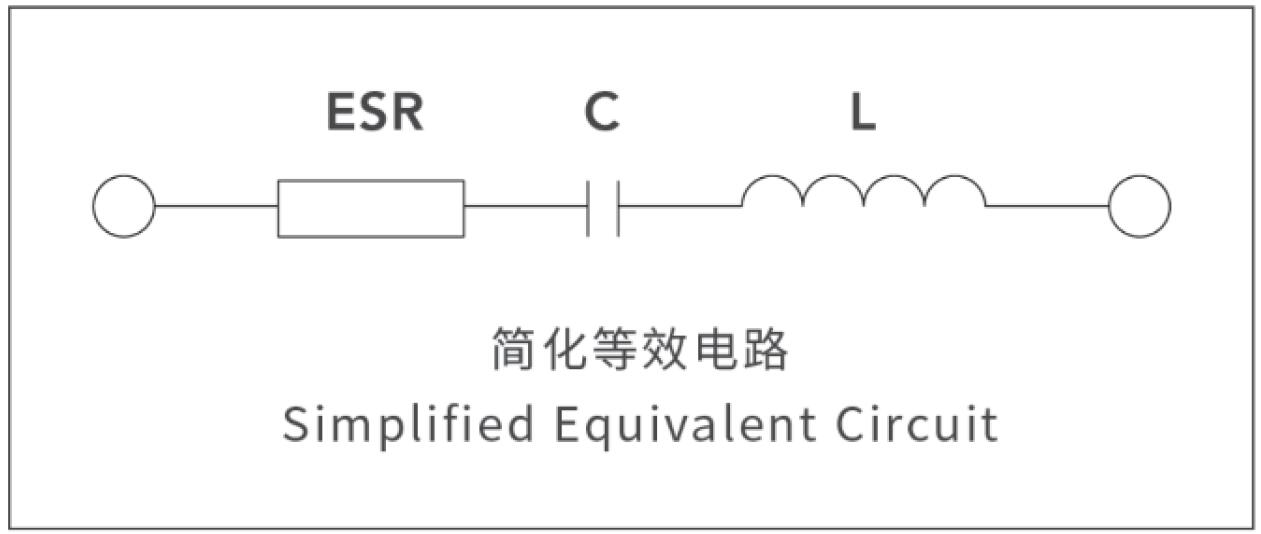
11. Dissipation factor and equivalent series resistance:
The dissipation factor or tangent of loss angle (tan δ) is the power loss of the capacitor divided by the reactive power of the capacitor at a sinusoidal voltage of specified frequency. The equivalent series resistance(ESR) is the resistive part of the equivalent circuit composed of capacitance, series resistance and inductance.